A) Relation tension – courant
|
Composant
|
Résistance |
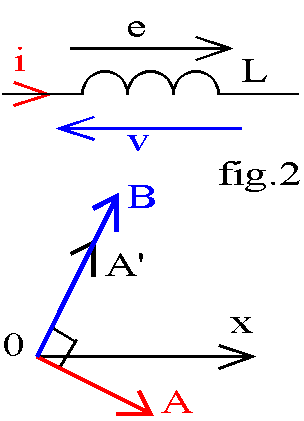
Inductance |
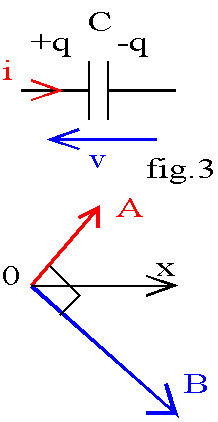
Condensateur |
|
Loi d’Olhm |
V(t) = R. i(t)
|
V(t) = L. di(t)/dt |
I(t) = C. dv(t)/dt |
|
Régime Périodique |
Vmoy = R.Imoy
Veff = R.Ieff
|
Vmoy = 0 |
Imoy = 0 |
|
|
|
| 
| 
|
|
|
V = R.I
|
V = j.L.w.I |
V = I/j.C.w. |
|
|
V = R.I
|
V = L.w.I |
V = I/C.w. |
|
Déphasage
|
0 |
π/2 |
-π/2 |
B) Impédance complexe
Z = V / I = (Z Ð j) = R + j. X
Y =1 /Z = I / V = (YÐ -j) = G + j. S
association en série : Z = S Zn
association en parallèle : Y = S Yn

