C’est la différence entre le total des avoirs et créances et le total des dettes pour une devise donnée.
Exemple : cas d’une entreprise d’import – export :
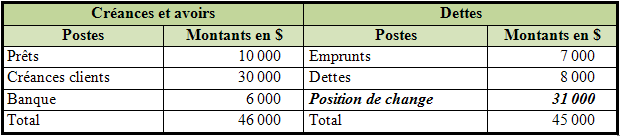
L’entreprise est exposée à un risque de change sur le montant de sa position de change soit 31 000 $.
La position de change calculée par échéance à 3 mois, 6 mois ou 1 an, est dite :
- courte quand les dettes sont supérieures aux créances et avoirs
- longue quand créances et avoirs sont supérieurs aux dettes.

